Most of us have heard of nuclear energy, but how much do you know about this form of electricity? When you’re presented with the words “nuclear energy”, some of the first images that may pop in your head might be of a nuclear bomb or an energy crisis such as Fukushima or Chernobyl. If these are your impressions of nuclear energy, then you’ll be surprised to learn that, when it comes to carbon dioxide emissions and other air pollutants, nuclear energy is nearly equal to other renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar.
Nuclear energy can be defined as the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. This energy can be used to produce electricity. Nuclear energy comes from mass-to-energy conversions that occur in the splitting of atoms. This source of energy can be produced in two ways: fission – when nuclei of atoms split into several parts – or fusion – when nuclei fuse together.
The nuclear energy harnessed around the world today to produce electricity is through nuclear fission, while the technology to generate electricity from fusion is in the R&D phase. This article will explore nuclear fission. When you split a uranium atom into two smaller atoms, it releases heat. This heat is used to produce steam, which turns enormous turbines in a nuclear plant. These turbines power generators that produce electricity. The steam then turns back into water and can be used over and over again.
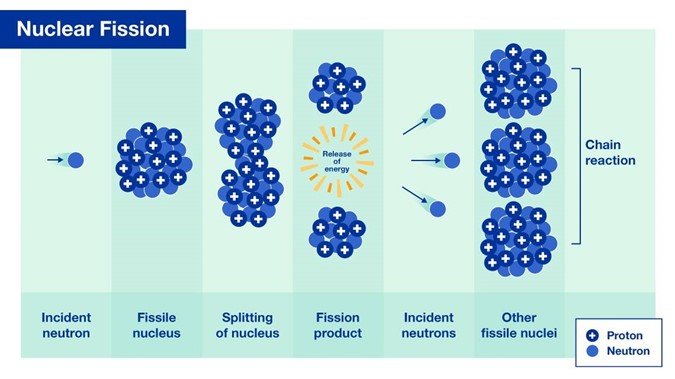
Nuclear power plants use the process of nuclear fission in which an atom is split in two to produce energy. These plants use large amounts of water for steam production and cooling. These power plants are the most efficient source of electricity. It is being used in more than 30 countries around the world. It is also used to power mars exploration rovers.

However, there is a huge scope for humankind as this is a renewable resource, the recent Ukraine crisis has shown that wars and reactors make for a dangerous mix, raising troubling questions for other simmering conflicts around the world: Israel and Iran, China and Taiwan, and North and South Korea, among others. All have large nuclear power or weapons plants, and all are at risk of war.
Disarmament is the best protection against such dangers but achieving this goal has been a tremendously difficult challenge.