According to scientists' predictions, our increasingly warming planet is expected to surpass a crucial temperature threshold for the first time in the coming years.
Based on current trends and factors such as human-generated emissions and a potential El Niño weather pattern, researchers estimate a 66% likelihood of exceeding the 1.5C global warming limit by 2027.
While the probability is increasing, scientists emphasize that if the threshold is breached, it will likely be a temporary situation, although it remains a cause for concern.
Exceeding the threshold would indicate that the world has warmed by 1.5C compared to the latter half of the 19th Century, a time prior to the significant rise in fossil fuel emissions due to industrialization.
Furthermore, surpassing this limit, even if only for a single year, is a concerning indication that the pace of global warming is accelerating rather than slowing down.
The value of 1.5C has become a symbolic representation in global climate change negotiations, as nations committed to making efforts to limit temperature increases to this level under the 2015 Paris agreement.
Should global temperatures consistently surpass 1.5C for a decade or two, the consequences of warming, such as prolonged heatwaves, more severe storms, and increased wildfires, would be significantly amplified.
However, it is important to note that exceeding the 1.5C threshold in one of the upcoming years does not necessarily mean that the Paris agreement's limit has been breached. Scientists emphasize that there is still time to mitigate global warming by substantially reducing emissions.
Starting from 2020, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has been providing an assessment of the probability of the global temperature surpassing the 1.5C threshold within a single year.
Initially, their prediction indicated a probability of less than 20% for breaching the 1.5C limit in the subsequent five years.
By the following year, this likelihood had escalated to 50%, and presently, it has risen to 66%. Scientists interpret this increase as a sign that surpassing the threshold is now considered "more likely than not."
What are the implications of exceeding the 1.5C threshold?
To gauge the global temperature before the widespread use of coal, oil, and gas, scientists utilize average temperature records from the period between 1850 and 1900.
Traditionally, scientists believed that a warming of approximately 2C would be the threshold for significant and detrimental consequences. However, in 2018, they revised this estimation substantially, highlighting that surpassing the 1.5C mark would have catastrophic implications for the world.
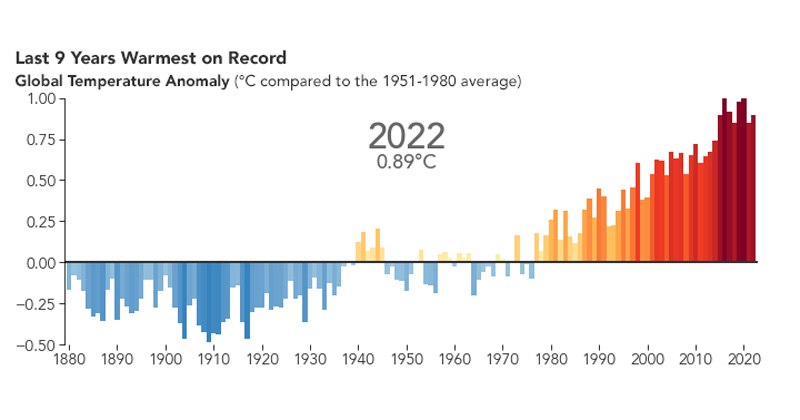
In recent decades, our increasingly warming planet has gradually pushed global temperatures upward. In 2016, which marked the warmest year on record, global temperatures were already 1.28C higher than the pre-industrial level.
However, researchers now predict that this record will be shattered, expressing 98% certainty that it will be surpassed before 2027.
Moreover, within the years leading up to that point, there is a strong likelihood that the 1.5C limit will be exceeded for the first time. This represents a significant milestone in human history, as stated by Prof Adam Scaife, the head of long-range forecasts at the Met Office, who compiles data from various weather and climate agencies worldwide. We are now on the verge of temporarily exceeding the 1.5C threshold, a scenario that has never occurred before.
During a news conference, the speaker highlighted that the mentioned statistic is likely the most striking, evident, and straightforward figure presented in the report.
The researchers emphasize that for the threshold defined in the Paris agreement to be officially crossed, temperatures would need to remain at or above 1.5C for a continuous period of 20 years.
WMO Secretary-General Prof. Petteri Taalas clarified, "This report does not imply a permanent breach of the 1.5C level specified in the Paris Agreement, which pertains to long-term warming over many years."
Nonetheless, Prof. Taalas cautioned that the WMO is raising the alarm regarding the escalating frequency of temporary breaches of the 1.5C limit.
What impact will El Niño have?
Two crucial factors come into play. Firstly, there is the persistent rise in carbon emissions resulting from human activities, which, despite a temporary decrease during the pandemic, continues to increase over time.
The second pivotal element is the anticipated occurrence of El Niño, a weather phenomenon that holds significant global implications.
Over the past three years, the world has been experiencing a La Niña event, which has somewhat mitigated climate warming effects.
The additional heat brought by El Niño is expected to raise the global temperature to a new peak in the upcoming year. Nevertheless, there remains uncertainty regarding when the event will occur and how significant it will be.
"It is important to highlight that our current forecasts for the development of El Niño this winter indicate a considerable impact," stated Professor Scaife in a briefing with reporters. "However, accurately predicting the intensity of subsequent events within the next five years is challenging. Thus, we cannot provide specific dates beyond the coming year. It is possible that a two and a half degree El Niño might occur in three or four years from now and have the desired effect."